Myasthenia Gravis: What Kind Of Disease Is It?

Myasthenia gravis is an autoimmune disease characterized mainly by weakening of voluntarily controlled muscles.
It is a pathology in which the body’s own immune system attacks the receptors in the muscles that allow them to move normally. In other words, the connection between these nerves and muscles is broken, interrupting their normal functioning.
The term myasthenia gravis comes from a Latin word and means “severe muscle weakness”. It is estimated to affect one in every 5,000 people. Although it can occur at any age, the incidence of the disease is higher in women under 40 years of age and men over 50 years of age.
It is a pathology that significantly injures the patient and is a very complex pathology for which medicine has not yet found a cure. However, we have a few treatments in our hands that, fortunately, help alleviate the symptoms of myasthenia gravis and improve the patient’s quality of life. In this article, we take a closer look at the origin, symptoms, and diagnosis of that disease.
What is myasthenia gravis?
To understand this pathology, we must first understand a little more about muscle function. Muscles have tiny receptors that receive chemical signals that come from the nerves. Normally, when we want to do a voluntary movement, these substances are released at the ends of the nerves. These agents act on muscle receptors, allowing the desired movement to occur with the required force and precision.
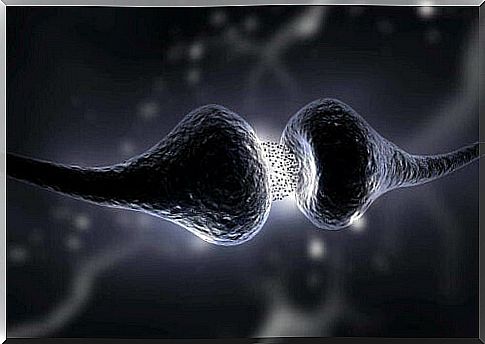
However, myasthenia gravis is characterized by the body’s own immune system being disrupted and attacking these muscle receptors. This in turn results in these chemicals no longer being able to activate the muscles normally, resulting in muscle weakening and fatigue.
Muscle weakness increases the more active the person with the disease is. Myasthenia gravis usually affects the muscles that control, for example, facial expressions, bites or swallowing. In some cases, it can even affect the respiratory muscles.
What are the symptoms of myasthenia gravis?
As mentioned earlier, the main symptom of the disease is muscle weakness. This weakness increases as more meat is used and decreases as it is used less. In other words, the muscle weakness caused by the disease facilitates rest and therefore its symptoms are usually mild in the mornings. Unfortunately, however, the symptoms worsen over time, and within a few years of the onset of the disease, the symptoms can already be really severe.
Myasthenia gravis can affect many different muscle groups, but the muscle groups it most commonly affects are:
- Eye muscles: Most patients with myasthenia gravis experience vision problems, such as seeing things in two. In addition, in many cases, they may have a drooping eyelid in one or both eyes.
- Most patients have difficulty speaking. The voice of a patient with myasthenia gravis is usually soft and resembles a tone of voice that passes through the nose.
- The swallowing process is disrupted or made more difficult: Simple movements such as chewing or swallowing become weak and complex processes. In practice, this means that the patient is at high risk of suffocation when consuming both solid food and liquid foods and beverages.
- Facial expressions disappear: Patients with myasthenia gravis are often unable to smile normally.
- On the other hand, the disease can also manifest as muscle weakness in the limbs or neck. If the patient’s limbs and / or neck suffer from muscle weakness caused by the disease, the ability to walk or maintain the head in a natural position is also impaired. As the neck muscles weaken, the head also tends to fall to one side or the other.
How can myasthenia gravis be diagnosed?
To diagnose myasthenia gravis, the physician must first hear all of the patient’s symptoms and familiarize themselves with various aspects of his or her medical history. Next, the doctor performs a thorough physical examination of the patient. In addition, in most cases, numerous additional tests are also required to confirm the diagnosis. For example, a physician may perform neurological examinations to measure the impairment or disruption of muscle strength and muscle tension, reflexes, coordination, and other characteristics indicative of the disease in question.
In addition, blood tests today provide quite useful information to confirm a correct diagnosis. As we have explained before, this is an autoimmune disease, so in most cases, specific antibodies can be found in a patient’s blood that indicate the presence of that disease. In some cases, the following tests may also be used to diagnose myasthenia gravis:
- Ice bag test : This is a useful test in cases where a hanging eyelid (or sagging eyelids) has been observed in a patient. A cold ice bag is placed on the patient’s eyelid for about two minutes, after which the doctor analyzes whether movement occurs in this area.
- Repetitive Nerve Stimulation: This test allows impulses to be sent through the nerves so the doctor can see if they are able to stimulate muscle movements.
Finally
Myasthenia gravis is a complex disease with significant muscle weakness; it can affect different parts of the body such as the eyes, limbs or respiratory muscles.
This is a serious pathology in which the muscles that weaken and, for example, the difficulty in swallowing and breathing, endanger the life of the person suffering from it in the worst case. The unfortunate fact is also that today’s medicine, as advanced as it is, has not yet been able to find a cure for this autoimmune disease. Therefore, it is essential that patients follow the doctor’s instructions carefully and turn to him or her with any symptom so that the doctor is able to build the most appropriate treatment for the patient’s condition to control the symptoms.