What Is Candida Auris?
Auris Candida is Candida yeast fungus belonging to the genus of which is still poorly understood, but which has given rise to considerable debate in the scientific community. The reason for this is that some of the strains of that yeast are resistant to all common antifungals and also to various control methods.
C. Auris can cause serious general infections and other inflammations and is particularly dangerous for hospital and inpatients with severe underlying conditions. For example, it is known to cause life-threatening sepsis. C. Unlike other yeasts, Auris can be transmitted from person to person by hand, from the surface of the environment, or through treatment and research equipment, for example. As a result, it has caused epidemics, especially in the intensive care units.
C. Auris was first identified in 2009 in Japan from a sample taken from a patient’s ear canal. However, it has since emerged that the first epidemic was already in South Korea in 2004-2009. Since then, epidemics have occurred in several countries.
Candida Auris cases worldwide
Thus, the first Candida Auris isolation was performed in Japan in 2009. Thereafter, researchers began to suspect that certain previously unidentified infections were likely due to the same pathogen. In the end, it became clear that the first C. Auris epidemic had already erupted in South Korea in 2004-2009.
Since then, discoveries have been made on four different continents and in more than 20 countries. Most cases have been in India, Central American countries, South Africa, Israel and Oman. C. Auris has so far been rare in Europe, but there has been a large-scale epidemic in both Spain and the United Kingdom. Earlier this year, the yeast C. Auris was first found in Finland, from a patient who had traveled to India.
Risk factors for severe Candida Auris infection
Not everyone who comes in contact with the yeast Candida Auris gets sick, and not everyone who gets it gets serious symptoms. A person can also act as a carrier of a fungus without becoming ill himself. Risk factors for severe C. Auris infection include:
- Severe illness
- Long time spent in the hospital
- Intensive care
- Previous antifungal treatment
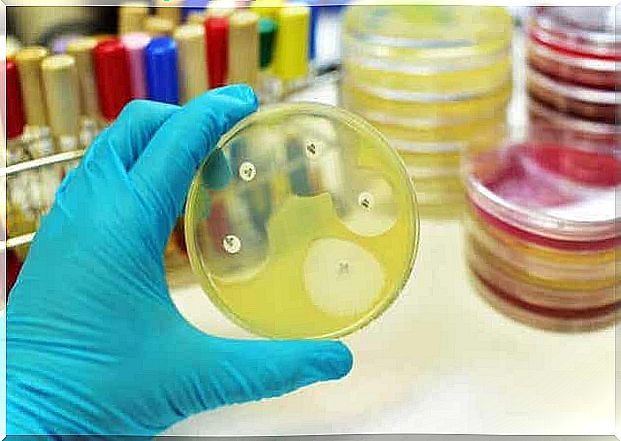
Drug resistance is a serious risk
Some strains of Candida Auris are known to be resistant to all three groups of antifungal agents, in addition to which the development of resistance during treatment is common. It is a persistent yeast that has also been found to be resistant to various control methods, for example in hospital environments. Where other pathogens have been killed from surfaces, for example with hydrogen peroxide, these substances have not been effective in C. auris.
Treatment of Candida Auris infection
Candida Auris infections are treated with yeast drugs, but as already mentioned above, this yeast easily develops resistance to the most common drugs. Fluconazole resistance is very common, in addition to which strains have been found to be resistant to all three major groups of antifungal drugs, i.e., azoles, echinocandins, and amphotericin B. As a result, overall mortality in epidemics has been high, up to 30-60%.