What Is Olaparib?
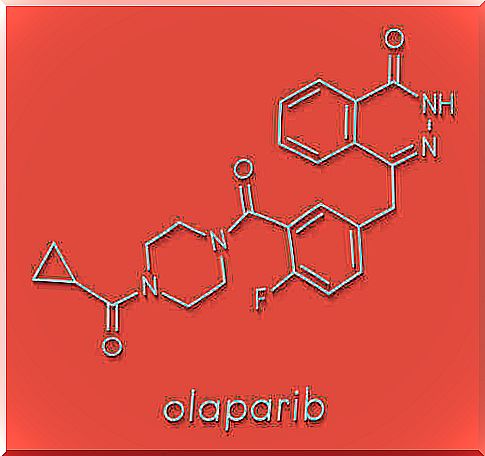
Olaparib is a chemotherapy drug that is specifically designed to treat advanced cancers. Its brand name is Lynparza, and it was originally developed by the pharmaceutical company AstraZeneca.
There are different pharmaceutical forms of olaparib, and doctors prescribe one or the other patient depending on the disease and the severity of the disease. For example, the tablet form is a form of monotherapy in the treatment of adult patients with high-grade epithelial ovarian and fallopian tube cancer. It also works in patients whose cancer has come back during platinum-based treatment.
In addition, shoulder bar capsules are also indicated for the treatment of cancers with the mutant gene BRCA. This gene plays an important role in the development of cancer, especially breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Note that olaparib capsules and tablets are not interchangeable due to different doses and biological differences. In addition, users of these medicines may experience the following side effects:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Neutropenia (a condition in the composition of the blood)
- Thrombocytopenia (lack of platelets)
- Dizziness
Shoulder bar and its mechanism of action
This medicine blocks the human enzymes that are responsible for repairing DNA. These enzymes are called PARP.
In vitro samples showed that it inhibits the growth of selected tumor cell lines and also tumor growth. It can be used both as a single treatment and in combination with previously established chemotherapies.
When olaparib binds to these DNA-related enzymes, it prevents DNA repair by several reactions. In healthy cells, this repair requires those with the BRCA1 and BCRA2 genes to function properly. Alternative error-prone repair pathways begin to activate, leading to increased genomic instability in cancer cells where these proteins do not function properly.
After several rounds of replication, genomic instability can reach intolerable levels in cancer cells. As a result, the cancer cells die. The reason for this is that there is a large amount of DNA damage in the cells compared to normal cells.
Olaparib administration after platinum therapy has been shown to be useful in studies in patients with a BRCA mutation and therefore lacking a functional BRCA protein. The results of the study showed that tumor growth and spread slowed. In addition, the patient’s chances of survival increased significantly compared to platinum alone.
Shoulder ribs and BRCA
As mentioned above, olaparib is mainly used to treat breast cancer, although it can also be used to treat other cancers. Especially in the case of advanced cancer or metastatic ovarian cancer.
For breast cancer, one of the most common molecular events in triple-negative breast cancers is a change in the function of the BRCA protein. This type of oncological cancer is one of the most aggressive cancers in women.
More than 80% of patients with a mutation in the BRCA1 gene have triple-negative breast cancer. The BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation has also been inherited in approximately 15% of patients with ovarian cancer and 5% of patients with breast, pancreatic or prostate cancer.

The shoulder bar is thus a PARP inhibitor. They are proteins that help repair damaged DNA. Because BRCA mutations can also affect the ability of DNA to repair itself, inhibiting this process with olaparib can lead to cancer cell death.
The researchers evaluated the effectiveness of olaparib as a single treatment and in combination with other chemotherapeutic agents in phase II clinical trials. In addition, its efficacy as monotherapy in patients with advanced breast cancer was a higher objective response rate.
Summary
Olaparib represents a new approach to antineoplastic therapy through PARP inhibition. In fact, it can address the unmet needs of patients with BRCA-related cancer.
Treatment is not easy because these neoplastic diseases are often quite advanced. They require a combination of treatments and proper monitoring. Ideally, the patient is supported by an oncology team that takes into account all the patient’s needs as well as the factors that affect treatment.